
GDPR Compliance
Today, users all over the world are increasingly worried about their privacy and how their personal information is being used in online applications. Considering this, there have been different regulations coming up to ensure privacy rights to the users and one of the big one that came was GDPR by the European Union.
What is GDPR?
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation. The General Data Protection Regulation is a regulation in EU law on data protection and privacy in the European Union (EU) and the European Economic Area (EEA). It also addresses the transfer of personal data outside the EU and EEA areas. To get a complete info on the regulation, you can visit here: GDPR Guidelines
What is meant by GDPR compliance?
IT is based on information and in the IT age, there have been countless instances of data breaches that impact organizations of all sizes. Information gets lost, stolen or otherwise released into the hands of people who were never intended to see it and those people often have bad intention.
Under the terms of GDPR, not only do organizations have to ensure that personal data is gathered legally and under strict conditions, but also they have to manage it by protecting it from misuse and exploitation, preserving the rights of data owners. Failure to do so can result in strict penalties and fines. Magnitude of the fines can be seen here: GDPR Fines
GDPR Principles
- Lawfulness, fairness and Transparency
- Purpose Limitation
- Data Minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage limitation
- Integrity and confidentiality (security)
- Accountability
More Info here: GDPR Principles
What does GDPR mean for users/citizens?
Because of the number of data breaches and hacks that occur, the reality for many is that some of their data like their personal email address, password, social security number, or confidential health records, etc can be exposed on the internet. Even the payment information have been stolen in multiple instances. Some of the key individual rights that have been defined under GDPR are:
- The right to be informed
- The right of access
- The right to rectification
- The right to erasure
- The right to restrict processing
- The right to data portability
- The right to object
- Rights in relation to automated decision making and profiling.
More Info here: GDPR Rights
Change in GDPR for user convenience
One of the major changes GDPR brings is providing consumers with a right to know when their data has been hacked. Organizations are required to notify the appropriate national bodies as soon as possible in order to ensure EU citizens can take appropriate measures to prevent their data from being abused. Consumers are also promised easier access to their own personal data in terms of how it is processed, with organizations required to detail how they use customer information in a clear and understandable way.
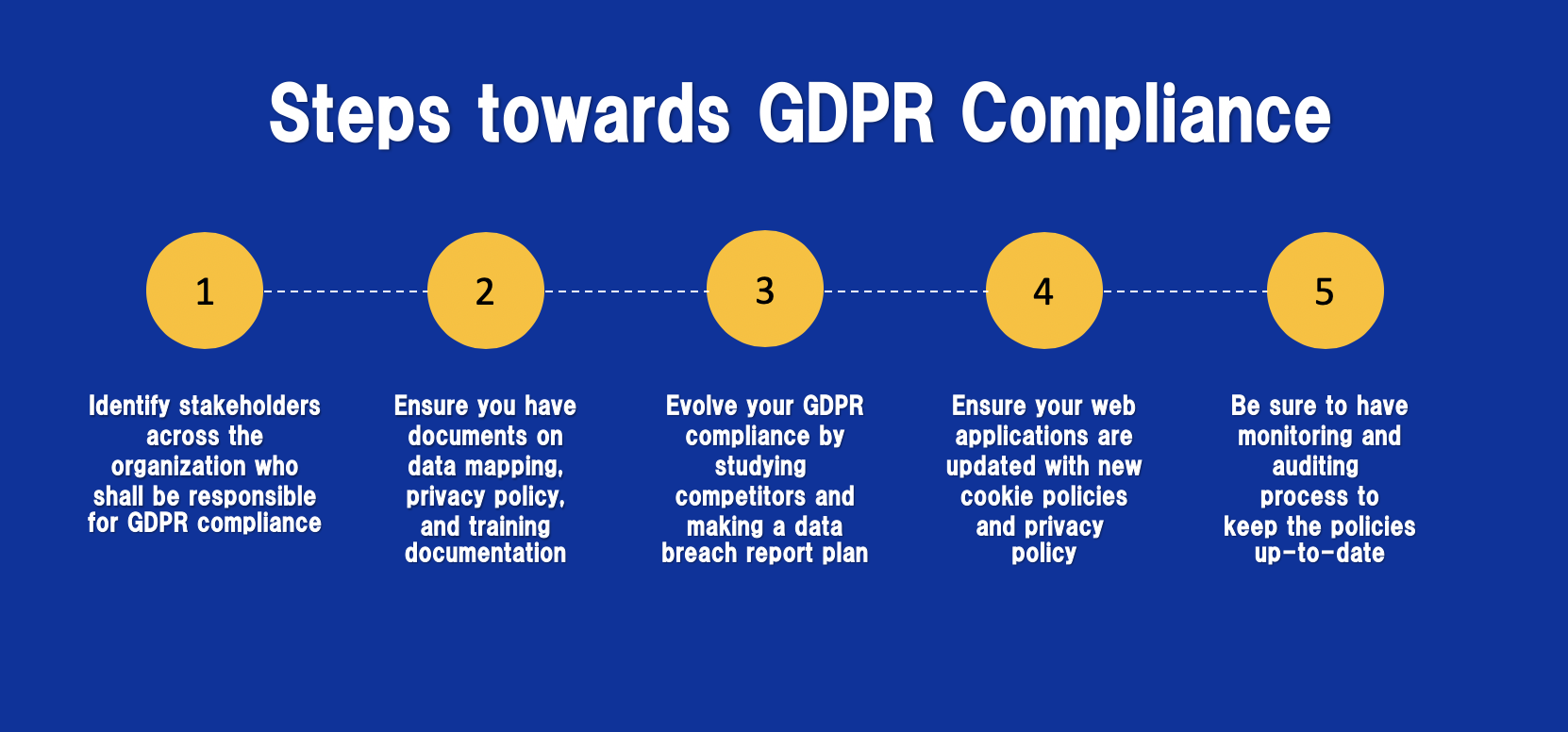
Common steps to become GDPR compliant:
There are five main steps in regarding to achieve GDPR compliance that are discussed below:
-
GDPR regarding key concepts and articles
Being GDPR compliant is not just about “fixing a website”. It must be a part of your entire organization. There are various stakeholders in any organization who can have access to user personal information. In most cases, there are different levels of key personnel (HR, IT, marketing, and security teams) that interact with customers’ data and therefore should be aware of the General Data Protection Regulation. It is not a single department responsibility. You need both technical and legal implementations.
-
What to do for GDPR compliance now
The list is not exhaustive and only describes basic things that can be ensured for moving towards GDPR compliant organization:
-
Data mapping
An important step towards compliance with GDPR is to understand how data moves in your organization. Documenting the way information flows in your company by making an inventory helps you demonstrate that you comply. A good starting point should be data map.
Mapping the flow of data will also help you identify areas that could cause GDPR compliance problems. You need to identify next how this information is processed, how long does it stay in the system, how is the information being transferred in and out of your network and also who all has access to it by any means. You also need to identify why you need that information and try to minimize the information you capture in your system in case you don’t need it.
-
Privacy Policy
Review and update your current Privacy Policy. Privacy Policy serves as a public statement about how the organization takes care of GDPR compliance, what all data they are collecting and how is it being used. The first step in the process will help you define a very elaborate Privacy Policy.
There can be few important pieces of information that can go into the Privacy Policy. The legal basis for collecting the data, retention periods for the data, the right to refuse when customers do not want their personal information to be captured, whether their data will be subject to automated decision making in or out of the application, and their rights under the GDPR.
Furthermore, you must provide the information in concise, easy to understand and clear language.
-
Training
The GDPR is a business change project – the people you work with need to understand the importance of data protection and be trained on the basic principles of the GDPR and the procedures being implemented for compliance.
-
Data mapping
-
GDPR compliance evolution
Organization admins responsible for managing the data should always cooperate with the Supervisory Authority regarding the fulfillment of their tasks.
Plan and schedule regular audits of data processing activities and security controls in your organization. Keep audit records of personal data kept in the system and maintain records regarding the audits for proof of consent. This serves as an excellent way to show that your organization has been actively focused on ensuring data privacy and compliance.
-
Check what other vendors are doing
Because GDPR defines guidelines and there is no fixed approach, the market will have to come up with different ways to ensure that data is in compliance without impacting user experience. A lot of companies innovate in the field and come up with new techniques to ensure compliance. Study your competitors or similar companies to identify what they are doing for GDPR compliance and discuss with your team responsible for GDPR compliance on how the team can incorporate the same in the organization.
-
Report data breaches
Even after taking precautions, breaches can occur and happens to the best of the companies. But having a disaster management plan is essential to ensure the damage is minimal. You should ensure you have the right procedures in place to detect report and investigate data breaches - not only internally but also to external agencies responsible. Be smart while setting up the data breach matrix based on data breach severity, the number of data subjects affected, type of personal data affected, etc.
Typically, you must report data breaches to the Supervisory Authority within 72 hours unless the personal data was anonymzed or encrypted.
-
Continue working on operational policies, procedures, and processes
GDPR compliance is not a one-time activity and requires continuous evolvement, adoption, planning and audits to ensure proactiveness in ensuring compliance. It is a continuous activity to make sure that the data you collect is safe and used with a proper scope that is important for your application. You should review the policies to ensure they cover all the rights of individuals, including how personal data will be deleted or provided electronically in a commonly used format.
-
Check what other vendors are doing
-
Website adjustments
Again, GDPR does not define any clear-cut steps on how to make your application compliant. They have defined the guidelines and the implementation is left to individual organization. Some would say that adjusting forms and getting consent for cookies fixes about 80% of the issues. However, keep in mind, this is not a rule to rely on as compliance differs for each organization individually and the organization needs to evaluate things in their context.
-
Monitor and audit
Let’s look at one final step to ensure you have all the policies and procedures in place for GDPR compliance. Now that you have defined and implemented all the policies, the responsibility does not end there. Audits and monitoring is a routine activity to ensure that the current policies and implementations are working and up-to-date.
General Data Protection Regulation is leaving lots of room for improvement when it comes to protecting individuals. This is why the future privacy Regulation will bring even more transparency, especially in Big Data, shedding some light on occurrence and purpose of analytics. This should be a good enough reason to monitor and audit your data on a regular basis.
We at Boolean Solutions can help you with GDPR compliance based on our previous experience with organizations. We have some templates and also have the technical know-how that can bring your application many steps closer to GDPR compliance.
